The altimeter is a pressure measuring device which gets its input from the static port.
The drop in pressure caused by an increase in elevation results in the dial turning clockwise. Conversely, the increase in pressure with decrease in elevation turns the dial counterclockwise.
The adjustment knob allows you to change the barometric pressure.
Reading the altimeter
Units of Measurement
Depending on such things as the manufacturer, the country of origin and even the age, the altimeter can use a different unit of measurement on its scale. Some altimeters can have 2 scales; hectopascals and inches of mercury.
Millibar/Hectopascal (mb / hPa): standard according to the Système International (SI). 1mb = 1hPa
Inches of Mercury (inHg): common in American aircraft
Millimetres of Mercury (mmHg): common in Russian aircraft
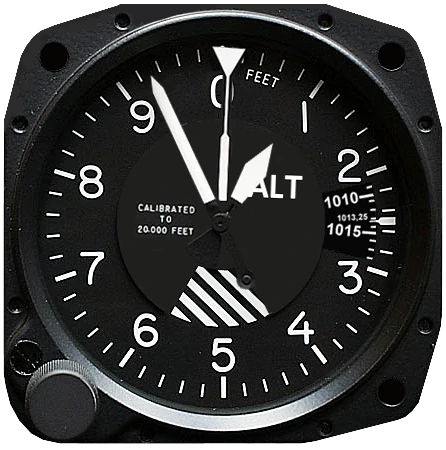
The dial

The long pointer reads 100 foot increments.
The short pointer reads 1,000 foot increments.
The thin needle reads 10,000 foot increments.
The Kollsman window shows the pressure scale selected by the adjustment knob.
Setting the altimeter
Pressure conditions can be expressed in different ways, each resulting in a different reading.
A set of Q-codes is used to indicate certain settings:
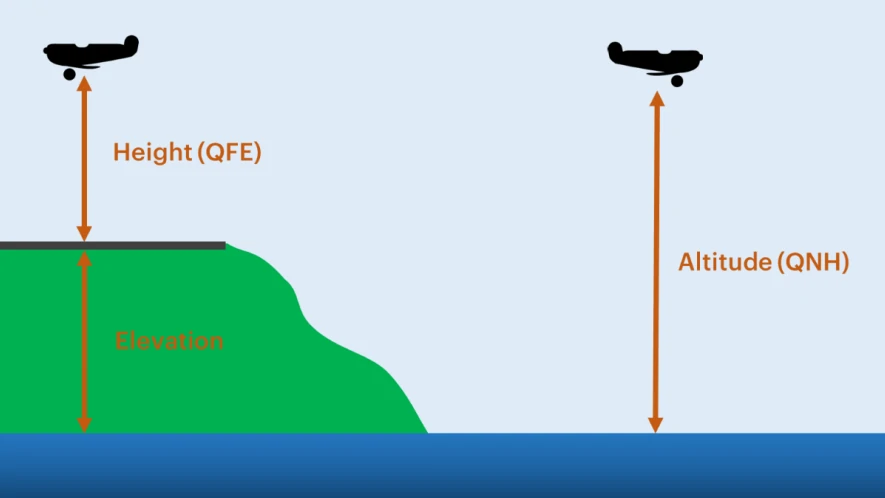
QFE is atmospheric pressure above ground level. For example, if you set the QFE of an airfield, then the altimeter reads zero when you are on the ground, and shows the height above the airfield when in the air.
QNH allows the altimeter to indicate the current local altitude above sea level. This means that the altitude of airfields and geographical features from a chart are applicable if the QNH is set correctly. For example, if the runway of an airfield is located at an elevation of 350 feet mean sea level (MSL), then the altimeter will show this altitude when the aircraft is on the ground.
QNE is atmospheric pressure value at mean sea level using ISA (International Standard Atmosphere). It is used to provide a common means of measuring flight level above the Transition Altitude by setting the altimeter to the Standard Pressure value (1013.25mb/hPa, 760mmHg, 29.92inHg).
The simple explanation
QFE: Your height relative to the local airfield pressure.
QNH: Your altitude above mean sea level.
Don’t be concerned with QNE, as you are unlikely ever to use it.